Is -8 A Whole Number
salachar
Sep 01, 2025 · 5 min read
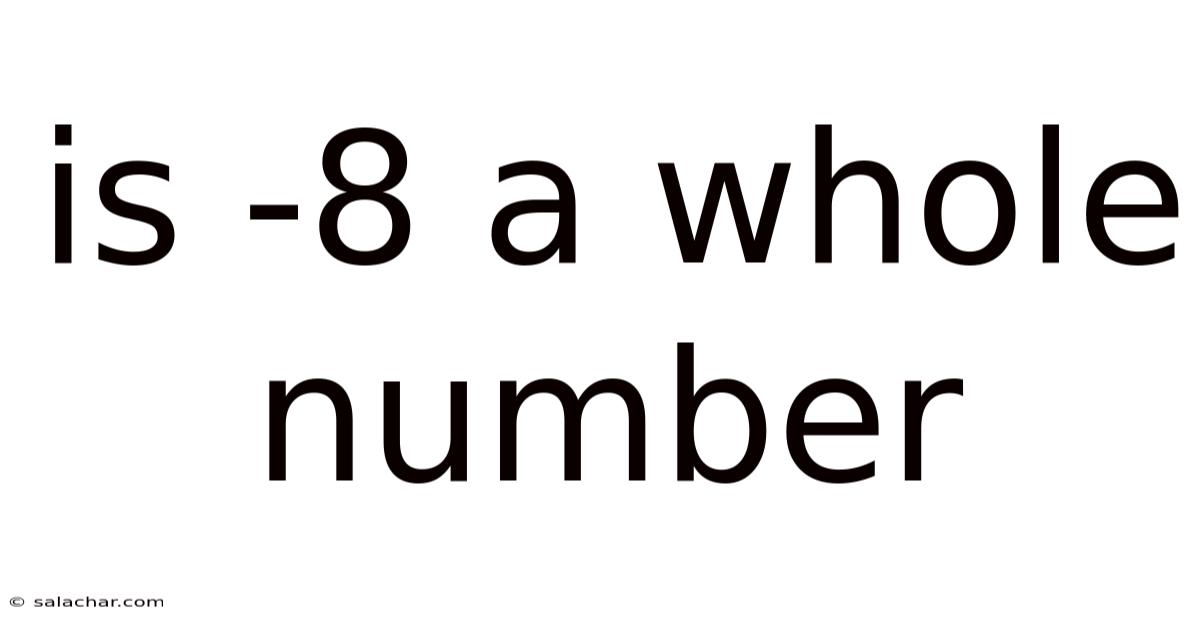
Table of Contents
Is -8 a Whole Number? Understanding Number Systems
Is -8 a whole number? This seemingly simple question opens a door to understanding the fascinating world of number systems and their classifications. The answer, while straightforward, requires a deeper exploration of the definitions and properties of different number sets. This article will not only answer the question definitively but also provide a comprehensive overview of number systems, helping you grasp the underlying concepts with clarity.
Introduction: Defining Whole Numbers
Before tackling the core question, let's define what we mean by "whole numbers." Whole numbers are the set of non-negative integers, starting from zero and extending infinitely in the positive direction. This means they include 0, 1, 2, 3, and so on. Crucially, whole numbers do not include negative numbers, fractions, or decimals. This is the key distinction that will determine whether -8 fits the definition.
Exploring Number Sets: A Hierarchy
Understanding whole numbers requires placing them within the broader context of the number system hierarchy. This hierarchy helps us visualize the relationships between different types of numbers:
-
Natural Numbers (Counting Numbers): These are the numbers we use for counting: 1, 2, 3, 4, and so on. Zero is not included in this set.
-
Whole Numbers: This set includes all natural numbers and zero (0, 1, 2, 3, ...).
-
Integers: This expands the whole numbers to include negative whole numbers: ..., -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, ...
-
Rational Numbers: This set encompasses all numbers that can be expressed as a fraction p/q, where p and q are integers and q is not zero. This includes all integers, as well as fractions and terminating or repeating decimals.
-
Irrational Numbers: These numbers cannot be expressed as a fraction of two integers. They have decimal representations that neither terminate nor repeat. Examples include π (pi) and √2 (the square root of 2).
-
Real Numbers: This is the set that includes all rational and irrational numbers. Essentially, it encompasses all numbers that can be plotted on a number line.
-
Complex Numbers: This set extends beyond real numbers to include imaginary numbers, which involve the square root of -1 (denoted as i).
The Case of -8: Why It's Not a Whole Number
Given the definition of whole numbers, the answer is clear: -8 is not a whole number. Whole numbers are defined as non-negative integers, and -8 is a negative integer. While it is an integer, it falls outside the set of whole numbers.
Misconceptions and Clarifications
It's crucial to address potential misunderstandings that might arise:
-
Confusion with Integers: Many people confuse whole numbers with integers. Remember, all whole numbers are integers, but not all integers are whole numbers. Integers encompass both positive and negative whole numbers, as well as zero.
-
The Importance of Definitions: Mathematics relies heavily on precise definitions. Understanding these definitions is paramount to avoiding confusion and ensuring accurate calculations and reasoning.
Practical Applications: Why Understanding Number Sets Matters
Understanding the distinctions between different number sets is not merely an academic exercise; it has practical implications in various fields:
-
Computer Programming: Programming languages often use specific data types to represent different kinds of numbers. Knowing whether a number is an integer or a floating-point number (which can represent decimals) is crucial for writing efficient and correct code.
-
Financial Calculations: In finance, accurately classifying numbers (e.g., as integers for whole dollar amounts or decimals for fractional amounts) is essential for precise financial calculations and reporting.
-
Scientific Modeling: Scientific models often involve different types of numbers, from integers representing discrete quantities to real numbers representing continuous measurements. Correctly categorizing numbers ensures the accuracy and reliability of the models.
Advanced Concepts: Number System Properties
Let's delve deeper into some key properties of number systems:
-
Closure: A number set is closed under an operation if performing that operation on any two numbers in the set always results in a number that is also in the set. For example, whole numbers are closed under addition (adding any two whole numbers results in another whole number), but not under subtraction (subtracting a larger whole number from a smaller one results in a negative number, which is not a whole number).
-
Commutativity: An operation is commutative if the order of the operands does not affect the result (a + b = b + a). Addition and multiplication are commutative for all the number sets we've discussed.
-
Associativity: An operation is associative if the grouping of operands does not affect the result ((a + b) + c = a + (b + c)). Addition and multiplication are associative for all the number sets we've discussed.
-
Distributivity: This property links addition and multiplication: a * (b + c) = (a * b) + (a * c). This holds true for all the number sets we've discussed.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Is 0 a whole number?
A1: Yes, 0 is a whole number. It is the smallest whole number.
Q2: Are all integers whole numbers?
A2: No, only non-negative integers are whole numbers. Negative integers are not whole numbers.
Q3: What is the difference between whole numbers and natural numbers?
A3: Natural numbers are the positive integers (1, 2, 3...), while whole numbers include zero in addition to the natural numbers (0, 1, 2, 3...).
Q4: Can a whole number be a fraction?
A4: No, whole numbers are integers; they cannot be expressed as fractions (except for trivial cases like 2/1, which is equivalent to the integer 2).
Q5: What type of number is -8?
A5: -8 is an integer and a rational number, but it is not a whole number or a natural number.
Conclusion: Mastering Number Systems
Understanding the different types of numbers and their properties is fundamental to success in mathematics and numerous other fields. While the answer to "Is -8 a whole number?" is a simple "no," the journey to arrive at that answer provides a valuable opportunity to solidify your understanding of number systems, their classifications, and their practical applications. Remember the key distinctions between natural numbers, whole numbers, integers, and rational numbers, and you'll be well-equipped to tackle more complex mathematical concepts with confidence. By grasping these foundational concepts, you lay a solid groundwork for future mathematical explorations.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Are Snails Classified As
Sep 04, 2025
-
Does Ice Cream Dehydrate You
Sep 04, 2025
-
How Many Miles Is 15km
Sep 04, 2025
-
Decimal Checkerboard Decimal Place Value
Sep 04, 2025
-
Very Poor Choice Of Words
Sep 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is -8 A Whole Number . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.